Top-Secret Document Reveals NSA Spied On Porn Habits As Part Of Plan To Discredit ‘Radicalizers’
Posted: 11/26/2013 11:20 pm EST | Updated: 12/02/2013 3:31 pm EST
WASHINGTON — The National Security Agency has been gathering records of online sexual activity and evidence of visits to pornographic websites as part of a proposed plan to harm the reputations of those whom the agency believes are radicalizing others through incendiary speeches, according to a top-secret NSA document. The document, provided by NSA whistleblower Edward Snowden, identifies six targets, all Muslims, as “exemplars” of how “personal vulnerabilities” can be learned through electronic surveillance, and then exploited to undermine a target’s credibility, reputation and authority.
The NSA document, dated Oct. 3, 2012, repeatedly refers to the power of charges of hypocrisy to undermine such a messenger. “A previous SIGINT” — or signals intelligence, the interception of communications — “assessment report on radicalization indicated that radicalizers appear to be particularly vulnerable in the area of authority when their private and public behaviors are not consistent,” the document argues.
Among the vulnerabilities listed by the NSA that can be effectively exploited are “viewing sexually explicit material online” and “using sexually explicit persuasive language when communicating with inexperienced young girls.”
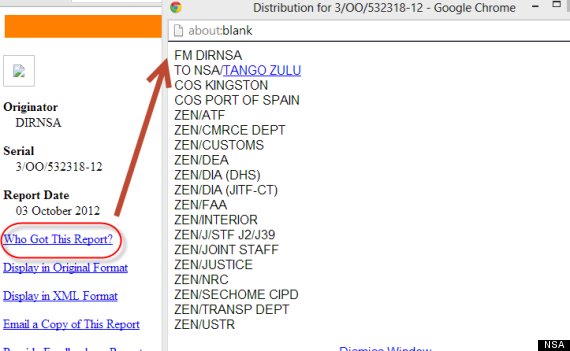
The Director of the National Security Agency — described as “DIRNSA” — is listed as the “originator” of the document. Beyond the NSA itself, the listed recipients include officials with the Departments of Justice and Commerce and the Drug Enforcement Administration.
“Without discussing specific individuals, it should not be surprising that the US Government uses all of the lawful tools at our disposal to impede the efforts of valid terrorist targets who seek to harm the nation and radicalize others to violence,” Shawn Turner, director of public affairs for National Intelligence, told The Huffington Post in an email Tuesday.
Yet Jameel Jaffer, deputy legal director of the American Civil Liberties Union, said these revelations give rise to serious concerns about abuse. “It’s important to remember that the NSA’s surveillance activities are anything but narrowly focused — the agency is collecting massive amounts of sensitive information about virtually everyone,” he said.
“Wherever you are, the NSA’s databases store information about your political views, your medical history, your intimate relationships and your activities online,” he added. “The NSA says this personal information won’t be abused, but these documents show that the NSA probably defines ‘abuse’ very narrowly.”
None of the six individuals targeted by the NSA is accused in the document of being involved in terror plots. The agency believes they all currently reside outside the United States. It identifies one of them, however, as a “U.S. person,” which means he is either a U.S. citizen or a permanent resident. A U.S. person is entitled to greater legal protections against NSA surveillance than foreigners are.
Stewart Baker, a one-time general counsel for the NSA and a top Homeland Security official in the Bush administration, said that the idea of using potentially embarrassing information to undermine targets is a sound one. “If people are engaged in trying to recruit folks to kill Americans and we can discredit them, we ought to,” said Baker. “On the whole, it’s fairer and maybe more humane” than bombing a target, he said, describing the tactic as “dropping the truth on them.”
Any system can be abused, Baker allowed, but he said fears of the policy drifting to domestic political opponents don’t justify rejecting it. “On that ground you could question almost any tactic we use in a war, and at some point you have to say we’re counting on our officials to know the difference,” he said.
In addition to analyzing the content of their internet activities, the NSA also examined the targets’ contact lists. The NSA accuses two of the targets of promoting al Qaeda propaganda, but states that surveillance of the three English-speakers’ communications revealed that they have “minimal terrorist contacts.”
In particular, “only seven (1 percent) of the contacts in the study of the three English-speaking radicalizers were characterized in SIGINT as affiliated with an extremist group or a Pakistani militant group. An earlier communications profile of [one of the targets] reveals that 3 of the 213 distinct individuals he was in contact with between 4 August and 2 November 2010 were known or suspected of being associated with terrorism,” the document reads.
The document contends that the three Arabic-speaking targets have more contacts with affiliates of extremist groups, but does not suggest they themselves are involved in any terror plots.
Instead, the NSA believes the targeted individuals radicalize people through the expression of controversial ideas via YouTube, Facebook and other social media websites. Their audience, both English and Arabic speakers, “includes individuals who do not yet hold extremist views but who are susceptible to the extremist message,” the document states. The NSA says the speeches and writings of the six individuals resonate most in countries including the United Kingdom, Germany, Sweden, Kenya, Pakistan, India and Saudi Arabia.
The NSA possesses embarrassing sexually explicit information about at least two of the targets by virtue of electronic surveillance of their online activity. The report states that some of the data was gleaned through FBI surveillance programs carried out under the Foreign Intelligence and Surveillance Act. The document adds, “Information herein is based largely on Sunni extremist communications.” It further states that “the SIGINT information is from primary sources with direct access and is generally considered reliable.”
According to the document, the NSA believes that exploiting electronic surveillance to publicly reveal online sexual activities can make it harder for these “radicalizers” to maintain their credibility. “Focusing on access reveals potential vulnerabilities that could be even more effectively exploited when used in combination with vulnerabilities of character or credibility, or both, of the message in order to shape the perception of the messenger as well as that of his followers,” the document argues.
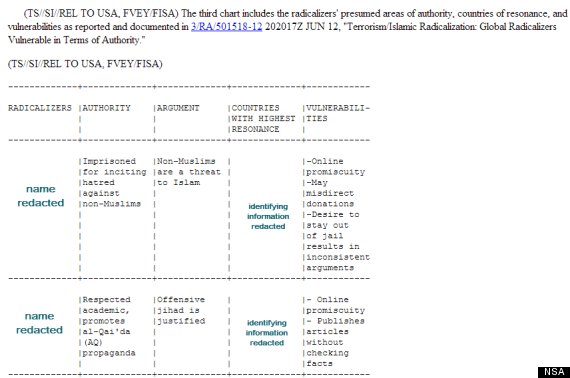
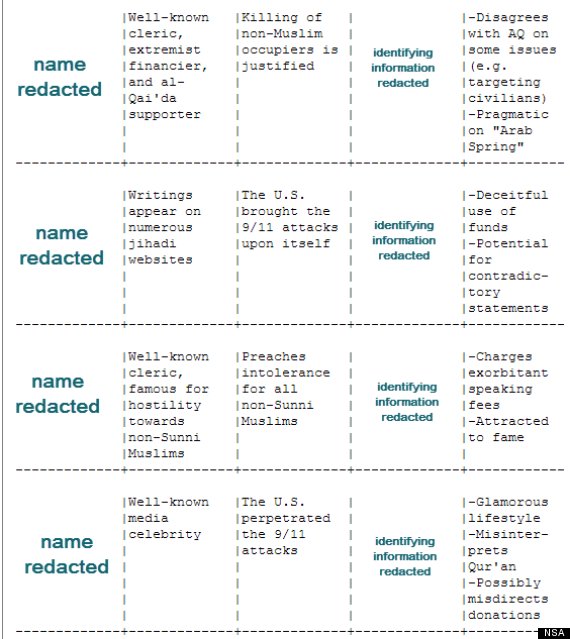
An attached appendix lists the “argument” each surveillance target has made that the NSA says constitutes radicalism, as well the personal “vulnerabilities” the agency believes would leave the targets “open to credibility challenges” if exposed.
One target’s offending argument is that “Non-Muslims are a threat to Islam,” and a vulnerability listed against him is “online promiscuity.” Another target, a foreign citizen the NSA describes as a “respected academic,” holds the offending view that “offensive jihad is justified,” and his vulnerabilities are listed as “online promiscuity” and “publishes articles without checking facts.” A third targeted radical is described as a “well-known media celebrity” based in the Middle East who argues that “the U.S perpetrated the 9/11 attack.” Under vulnerabilities, he is said to lead “a glamorous lifestyle.” A fourth target, who argues that “the U.S. brought the 9/11 attacks on itself” is said to be vulnerable to accusations of “deceitful use of funds.” The document expresses the hope that revealing damaging information about the individuals could undermine their perceived “devotion to the jihadist cause.”
The Huffington Post is withholding the names and locations of the six targeted individuals; the allegations made by the NSA about their online activities in this document cannot be verified.
The document does not indicate whether the NSA carried out its plan to discredit these six individuals, either by communicating with them privately about the acquired information or leaking it publicly. There is also no discussion in the document of any legal or ethical constraints on exploiting electronic surveillance in this manner.
While Baker and others support using surveillance to tarnish the reputation of people the NSA considers “radicalizers,” U.S. officials have in the past used similar tactics against civil rights leaders, labor movement activists and others.
Under J. Edgar Hoover, the FBI harassed activists and compiled secret files on political leaders, most notably Martin Luther King, Jr. The extent of the FBI’s surveillance of political figures is still being revealed to this day, as the bureau releases the long dossiers it compiled on certain people in response to Freedom of Information Act requests following their deaths. The information collected by the FBI often centered on sex — homosexuality was an ongoing obsession on Hoover’s watch — and information about extramarital affairs was reportedly used to blackmail politicians into fulfilling the bureau’s needs.
Current FBI Director James Comey recently ordered new FBI agents to visit the Martin Luther King, Jr. Memorial in Washington to understand “the dangers in becoming untethered to oversight and accountability.”
James Bamford, a journalist who has been covering the NSA since the early 1980s, said the use of surveillance to exploit embarrassing private behavior is precisely what led to past U.S. surveillance scandals. “The NSA’s operation is eerily similar to the FBI’s operations under J. Edgar Hoover in the 1960s where the bureau used wiretapping to discover vulnerabilities, such as sexual activity, to ‘neutralize’ their targets,” he said. “Back then, the idea was developed by the longest serving FBI chief in U.S. history, today it was suggested by the longest serving NSA chief in U.S. history.”
That controversy, Bamford said, also involved the NSA. “And back then, the NSA was also used to do the eavesdropping on King and others through its Operation Minaret. A later review declared the NSA’s program ‘disreputable if not outright illegal,'” he said.
Baker said that until there is evidence the tactic is being abused, the NSA should be trusted to use its discretion. “The abuses that involved Martin Luther King occurred before Edward Snowden was born,” he said. “I think we can describe them as historical rather than current scandals. Before I say, ‘Yeah, we’ve gotta worry about that,’ I’d like to see evidence of that happening, or is even contemplated today, and I don’t see it.”
Jaffer, however, warned that the lessons of history ought to compel serious concern that a “president will ask the NSA to use the fruits of surveillance to discredit a political opponent, journalist or human rights activist.”
“The NSA has used its power that way in the past and it would be naïve to think it couldn’t use its power that way in the future,” he said.
Adriana Usero and Ryan J. Reilly contributed reporting
Arguments for which radicalizers are being targeted:
Where the report was sent:
Intelligence gleaned from electronic surveillance:
ALSO ON HUFFPOST:

-
Edward Snowden
This June 9, 2013, file photo provided by The Guardian in London shows Edward Snowden, who worked as a contract employee for the National Security Agency, in Hong Kong. (AP Photo/The Guardian, Glenn Greenwald and Laura Poitras, File)
-
Edward Snowden
In this image made from video released by WikiLeaks on Oct. 11, 2013, former National Security Agency systems analyst Edward Snowden speaks during a presentation ceremony for the Sam Adams Award in Moscow. (AP Photo)
-
Edward Snowden
A frame grab made from AFPTV footage, reportedly taken on Oct. 9, 2013, shows U.S. intelligence leaker Edward Snowden speaking during his dinner with a group of four retired U.S. intelligence workers and activists at a luxurious room in an unidentified location. (AFPTV/AFP/Getty Images)
-
Edward Snowden
In this image made from video released by WikiLeaks on Oct. 11, 2013, former National Security Agency systems analyst Edward Snowden smiles during a presentation ceremony for the Sam Adams Award in Moscow. (AP Photo)
-
Edward Snowden
In this image made from video released by WikiLeaks on Oct. 11, 2013, Edward Snowden (center) receives the Sam Adams Award in Moscow. (AP Photo)
-
Edward Snowden
This photo, taken June 9, 2013, in Hong Kong, provided by The Guardian in London shows Edward Snowden, who worked as a contract employee for the National Security Agency. (AP Photo/The Guardian)
-
Edward Snowden
This handout file photo taken on July 12, 2013, and made available by Human Rights Watch shows NSA leaker Edward Snowden during his meeting with Russian activists and officials at Sheremetyevo airport, Moscow. (AP Photo/Tatyana Lokshina, Human Rights Watch HO, file)
Snowden: An Open Letter to the People of Brazil
An Open Letter to the People of Brazil
12/16/2013 – 16h22
EDWARD SNOWDEN
Atualizado em 17/12/2013 às 08h11.
Six months ago, I stepped out from the shadows of the United States Government’s National Security Agency to stand in front of a journalist’s camera.
Espionage Whistleblower Edward Snowden to Seek Asylum in Brazil
I shared with the world evidence proving some governments are building a world-wide surveillance system to secretly track how we live, who we talk to, and what we say.
I went in front of that camera with open eyes, knowing that the decision would cost me family and my home, and would risk my life. I was motivated by a belief that the citizens of the world deserve to understand the system in which they live.
My greatest fear was that no one would listen to my warning. Never have I been so glad to have been so wrong. The reaction in certain countries has been particularly inspiring to me, and Brazil is certainly one of those.
At the NSA, I witnessed with growing alarm the surveillance of whole populations without any suspicion of wrongdoing, and it threatens to become the greatest human rights challenge of our time.
The NSA and other spying agencies tell us that for our own “safety”-for Dilma’s “safety,” for Petrobras’ “safety”-they have revoked our right to privacy and broken into our lives. And they did it without asking the public in any country, even their own.
Today, if you carry a cell phone in Sao Paolo, the NSA can and does keep track of your location: they do this 5 billion times a day to people around the world.
When someone in Florianopolis visits a website, the NSA keeps a record of when it happened and what you did there. If a mother in Porto Alegre calls her son to wish him luck on his university exam, NSA can keep that call log for five years or more.
They even keep track of who is having an affair or looking at pornography, in case they need to damage their target’s re*tion.
American Senators tell us that Brazil should not worry, because this is not “surveillance,” it’s “data collection.” They say it is done to keep you safe. They’re wrong.
There is a huge difference between legal programs, legitimate spying, legitimate law enforcement – where individuals are targeted based on a reasonable, individualized suspicion – and these programs of dragnet mass surveillance that put entire populations under an all-seeing eye and save copies forever.
These programs were never about terrorism: they’re about economic spying, social control, and diplomatic manipulation. They’re about power.
Many Brazilian senators agree, and have asked for my assistance with their investigations of suspected crimes against Brazilian citizens.
I have expressed my willingness to assist wherever appropriate and lawful, but unfortunately the United States government has worked very hard to limit my ability to do so — going so far as to force down the Presidential Plane of Evo Morales to prevent me from traveling to Latin America!
Until a country grants permanent political asylum, the US government will continue to interfere with my ability to speak.
Six months ago, I revealed that the NSA wanted to listen to the whole world. Now, the whole world is listening back, and speaking out, too. And the NSA doesn’t like what it’s hearing.
The culture of indiscriminate worldwide surveillance, exposed to public debates and real investigations on every continent, is collapsing.
Only three weeks ago, Brazil led the United Nations Human Rights Committee to recognize for the first time in history that privacy does not stop where the digital network starts, and that the mass surveillance of innocents is a violation of human rights.
The tide has turned, and we can finally see a future where we can enjoy security without sacrificing our privacy. Our rights cannot be limited by a secret organization, and American officials should never decide the freedoms of Brazilian citizens.
Even the defenders of mass surveillance, those who may not be persuaded that our surveillance technologies have dangerously outpaced democratic controls, now agree that in democracies, surveillance of the public must be debated by the public.
My act of conscience began with a statement: “I don’t want to live in a world where everything that I say, everything I do, everyone I talk to, every expression of creativity or love or friendship is recorded.
That’s not something I’m willing to support, it’s not something I’m willing to build, and it’s not something I’m willing to live under.”
Days later, I was told my government had made me stateless and wanted to imprison me. The price for my speech was my passport, but I would pay it again: I will not be the one to ignore criminality for the sake of political comfort. I would rather be without a state than without a voice.
If Brazil hears only one thing from me, let it be this: when all of us band together against injustices and in defense of privacy and basic human rights, we can defend ourselves from even the most powerful systems.